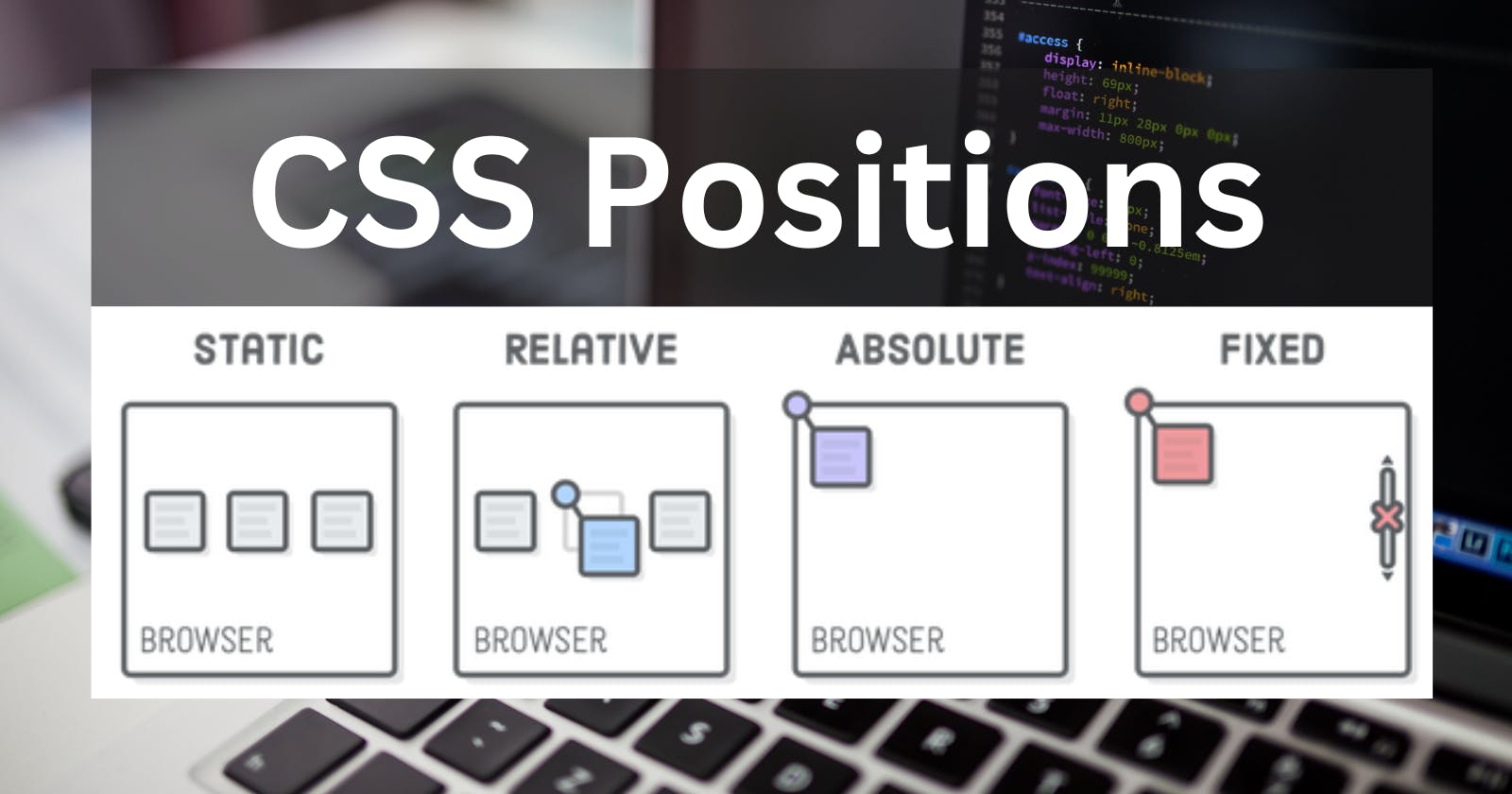
The position CSS property sets how an element is positioned in a document. The top, right, bottom, and left properties determine the final location of positioned elements.
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element. There are five different position values:
- static
- relative
- fixed
- absolute
- sticky
position: static;
- An element with
position: static;is not positioned in any special way. - The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have no effect.
- This is the default value.
position: relative;
- An element with
position: relative;is positioned relative to its normal position. - Setting the top, right, bottom and left properties of a relatively-positioned element will cause it to be adjusted away from its normal position. Other content will not be adjusted to fit into any gap left by the element.
position: fixed;
- An element with
position: fixed;is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled. - The top, right, bottom, and left properties are used to position the element.
- A fixed element does not leave a gap in the page where it would normally have been located.
position: absolute;
- An element with
position: absolute;is positioned relative to it's parent. - Absolute positioned elements are removed from the normal flow and can overlap elements.
position: sticky;
- An element with
position: sticky;is positioned based on the user's scroll position. - A sticky element toggles between relative and fixed, depending on the scroll position. It is positioned relative until a given offset position is met in the viewport - then it "sticks" in place.
Usecase of CSS Position Property
- If you want to add texts inside your image
Demo
Reference
Thanks for reading